- Refresh
- Contact
- Share
- Follow me
- Feedback
- Install
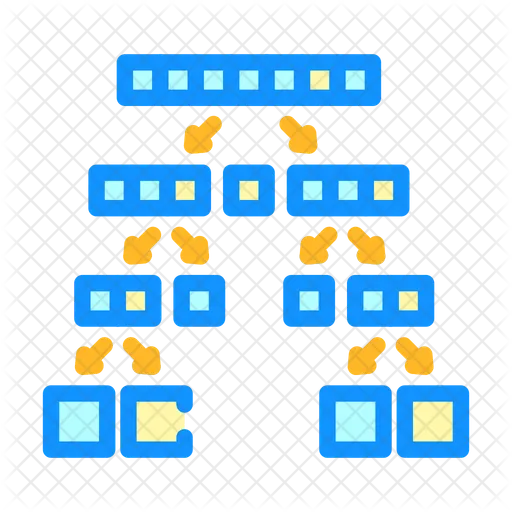
Enter an array separated by commas as : 16,15,15,10,1 or just press the hand icon to generate a random array then press enter or Sort button. Sorting will start and you can watch each pass as it gets sorted. When it shows green it means the two of them are being compared when red shows, it means the left number is greater than right number so it needs swapping The blue color means the number is at its correct position and thus sorted it will continue to check other numbers until it reaches end.
Quick sort was developed by Tony Hoare in 1960. It is a divide-and-conquer algorithm that is efficient for large datasets. Quick sort has become one of the most widely used sorting algorithms due to its performance in practice and its ability to sort in place.
O(n log n) – When the pivot divides the array into
nearly equal halves.O(n log n) – The average case performance is
efficient.O(n2) – Occurs when the smallest or largest
element
is always chosen as the pivot.Space Complexity: O(log n) – Due to the recursive stack space used
during the algorithm's execution.
function quickSort(arr, low, high):
if low < high:
pi = partition(arr, low, high)
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1)
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high)
function partition(arr, low, high):
pivot = arr[high]
i = low - 1
for j from low to high - 1:
if arr[j] <= pivot:
i = i + 1
swap arr[i] and arr[j]
swap arr[i + 1] and arr[high]
return i + 1Quick sort is a highly efficient sorting algorithm that utilizes the divide-and-conquer strategy.
Despite its worst-case time complexity of O(n2), it is widely used due to
its
average-case efficiency and practical performance.
// C code for Quick Sort
#include <stdio.h>
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (arr[j] < pivot) {
i++;
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
int temp = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
quickSort(arr, low, i);
quickSort(arr, i + 2, high);
}
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {16, 15, 15, 10, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Before sorting: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
printf("\nAfter sorting: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}